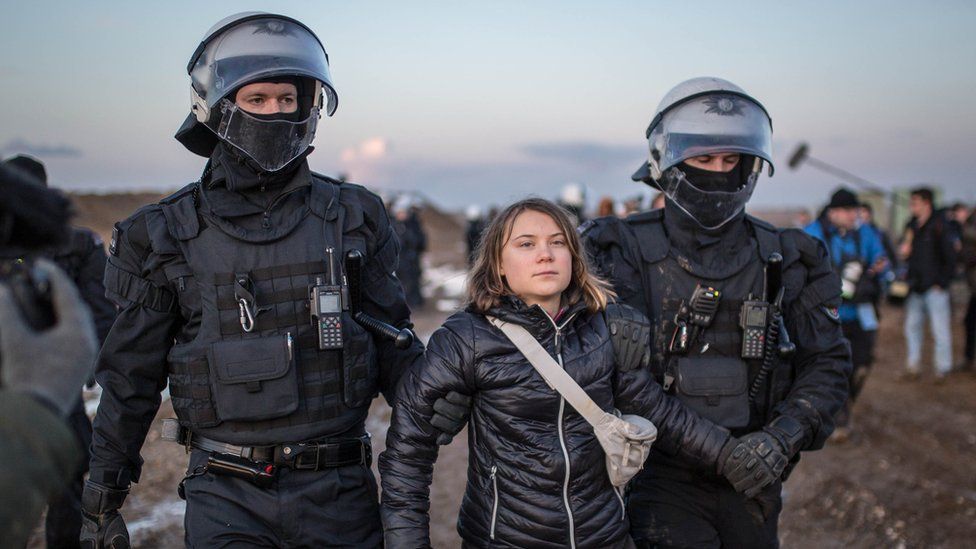
Swedish climate activist Greta Thunberg returns to Davos on Thursday to press her battle against fossil fuels at the annual confab of the global business and political elite.
Two days after police briefly detained her at a protest against a coal mine in Germany, Thunberg and other young campaigners will take part in a debate with the head of the International Energy Agency (IEA), Fatih Birol, on the sidelines of the World Economic Forum.
The 20-year-old Swede made a splash when she attended the forum as a teenager in January 2020, warning that “our house is still on fire” and complaining that her demands had been “completely ignored”.
Then-US president Donald Trump used his speech at the same forum to bash “the perennial prophets of doom” as Thunberg looked on from the audience.
This week, she and fellow activists Helena Gualinga of Ecuador, Vanessa Nakate of Uganda and Luisa Neubauer of Germany launched an online petition demanding that energy firms stop any new oil, gas or coal extraction projects — or face possible legal action.
More than 870,000 people had signed the petition by late Wednesday.
“Enough is enough,” Gualinga told AFP earlier this week. “We have to leave oil under the earth.”
The four campaigners will be among the panellists to discuss with Birol on Thursday calls to end new investments in fossil fuels and what should be done to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, organisers said.
The IEA, which advises governments, said in a report in October that the energy crisis triggered by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine was causing changes that could hasten the transition to a “more sustainable and secure energy system”.
– Big Oil’s ‘big lie’ –
“I agree with her efforts to stop that coal mine,” Gore told a panel discussion on global warming, adding that young people around the world despaired of efforts by leaders to tackle the climate crisis.
“We are not winning” the fight against global warming, he said.
Climate change is a major topic at the World Economic Forum, where businesses and governments have come under pressure to do more to ensure that the world meets the increasingly elusive goal of limiting warming to 1.5C.